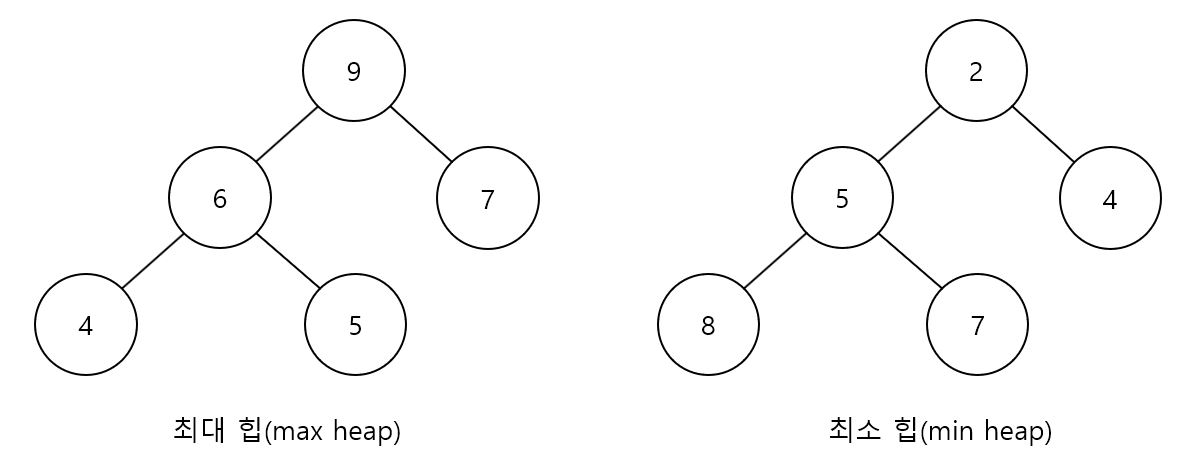
개념
완전 이진 트리입니다.
자식 노드의 키값과 부모 노드의 키값은 대소관계를 가집니다.
부모 노드의 키값이 자식 노드의 키값보다 클 시 최대 힙(max heap)이라 부르고 반대일 시 최소 힙(min heap)라고 부릅니다.
노드 값을 얻는 법
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 값 -> index * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 값 -> index * 2 + 1
- 부모 노드 값 -> index / 2
장점
- push와 pop을 진행할 시 시간 복잡도는 \(O(log_2n)\)입니다. 하지만 연결리스트를 이용할 시 \(O(n)\)입니다. 즉 힙의 속도가 더욱 빠릅니다. -> 우선순위 큐를 힙으로 구현하는 이유입니다.
- 시간복잡도가 \(O(log_2n)\)인 이유는 트리의 높이만큼 연산을 수행하기 때문입니다. 이진 트리이므로 데이터가 2배 늘어날 시 연산횟수는 1회 증가합니다.
소스 코드 (구현)
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class heap
{
private:
int length = 0;
T array[100];
function<int(T,T)> comp;
public:
heap() = delete;
heap(function<int(T,T)> cp) // 정렬방식 저장
{
length = 0;
comp = cp;
}
bool empty() const
{
if(length == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void push(T data)
{
if(length >= 100)
{
cout << "ERROR: Memory Is Full" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
int idx = length + 1;
while (idx != 1)
{
if(comp(data, array[idx / 2]) > 0)
{
array[idx] = array[idx / 2];
idx /= 2;
}
else
break;
}
array[idx] = data;
length += 1;
}
void pop()
{
if(empty())
{
cout << "ERROR: Memory Is Not Exist" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
T lastNode = array[length];
int parentIdx = 1;
int childIdx;
while (childIdx = GetPriChild(parentIdx))
{
if(comp(lastNode, array[childIdx]) >= 0)
break;
array[parentIdx] = array[childIdx];
parentIdx = childIdx;
}
array[parentIdx] = lastNode;
length -= 1;
}
T operator[](int idx) const { return array[idx]; }
int size() const { return length; }
private:
int GetPriChild(int idx) const // 우선 순위가 높은 자식 노드를 반환
{
if(idx * 2 > length)
return 0;
else if(idx * 2 == length)
return idx * 2;
else
{
if(comp(array[idx * 2], array[idx * 2 + 1]) < 0)
return idx * 2 + 1;
else
return idx * 2;
}
}
};Heap.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Heap.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
auto func = [](int data1, int data2)->int { return data2 - data1; };
heap<int> h(func);
h.push(1);
h.push(5);
h.push(2);
h.push(3);
h.push(4);
for (int i = 1; i <= h.size(); i++)
{
cout << h[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
while (!h.empty())
h.pop();
return 0;
}- ADT와 원리
- bool empty()
- length = 0일 시 true를 아닐 시 false를 반환합니다. (true를 반환할시 힙이 비어있다는 뜻입니다.)
- void push(T data)
- 마지막 노드에 추가한 후 부모 노드와 비교하면서 자리를 찾습니다.
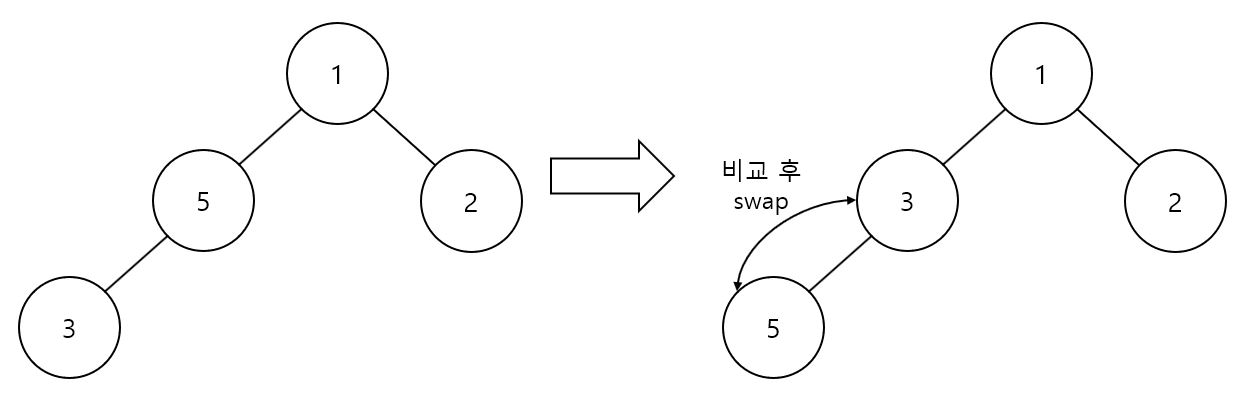
- 마지막 노드에 추가한 후 부모 노드와 비교하면서 자리를 찾습니다.
- void pop()
- 루트 노드를 삭제 후 마지막 노드를 루트 노드로 이동시켜 자식 노드 중 우선순위가 높은 노드(GetPriChild)와 비교하면서 자리를 찾습니다.
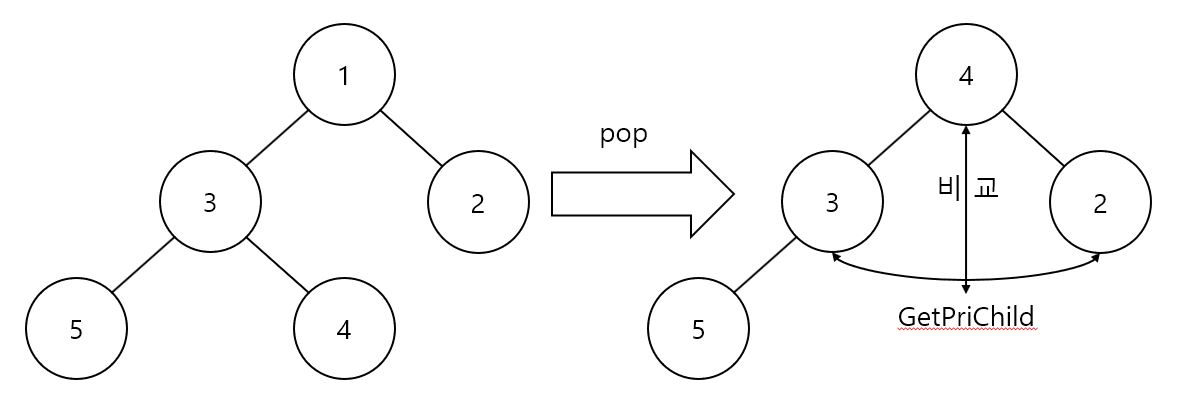
- 루트 노드를 삭제 후 마지막 노드를 루트 노드로 이동시켜 자식 노드 중 우선순위가 높은 노드(GetPriChild)와 비교하면서 자리를 찾습니다.
- int size() const
- 채워져있는 노드의 개수를 반환합니다.
- bool empty()
'알고리즘 Algorithm > 자료구조 Data structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 정렬 (sort) : 버블 정렬 (Bubble sort) (0) | 2021.02.24 |
|---|---|
| 우선순위 큐 (Priority queue) - [C++ STL] (0) | 2021.02.19 |
| 이진 트리 (Binary Tree) (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| 트리 (Tree) (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| 덱 (Deque) (0) | 2021.02.09 |


